This is a simple note to myself of how to remove Docker from Ubuntu or Raspberry Pi OS (previously called Raspbian). Credit goes to Mayur Bhandare on Stack Exchange. I also added some explanation to some of the commands so you will have a better understanding of what they’re doing.
1. Identify which Docker package have you installed
dpkg -l | grep -i docker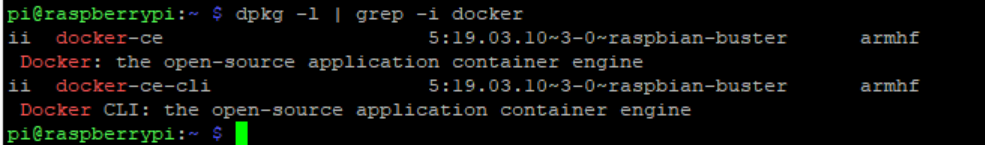
The dpkg command is a package management command in Debian. Just like apt-get in Ubuntu, a Linux distro based on Debian. Since Raspberry Pi OS is also a descendant of Debian, this will work just fine. The above command is basically saying, give me a list of packages that contains the word “docker” in them.
2. Remove the packages
For me, I’ve only installed docker-ce and docker-ce-cli. So I will run the following commands.
sudo apt-get purge -y docker-ce docker-ce-clisudo apt-get autoremove -y --purge docker-ce docker-ce-cliIf you have more docker packages installed, you can add those packages names to the end of the commands above. For example:
sudo apt-get purge -y docker-engine docker docker.io docker-ce docker-ce-cli
sudo apt-get autoremove -y --purge docker-engine docker docker.io docker-ce The “-y” flag here is to answer “yes” to the command prompt when it asks you whether to remove a package. You can choose to remove the “-y” flag. Then you’ll see prompts like the following and you have to manually answer yes or y for every package.
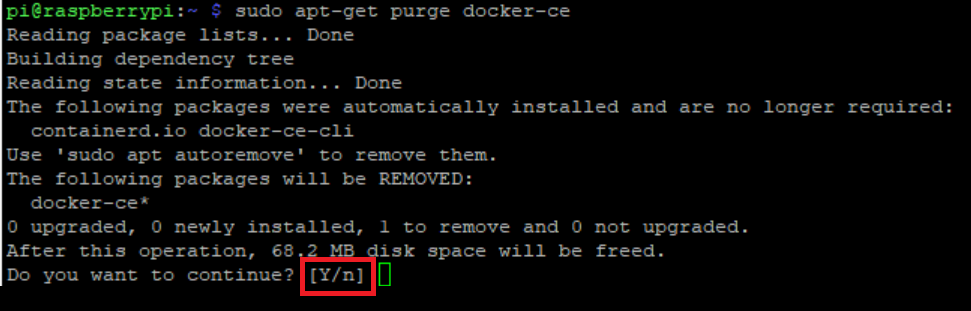
3. Remove all the Docker related files
After that, you might want to remove all the Docker images, containers, volumes, and configurations. This is how:
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker /etc/docker
sudo rm /etc/apparmor.d/docker
sudo groupdel docker
sudo rm -rf /var/run/docker.sockThe “-rf ” flag is a combination of the “-r” and “-f” flags. “-r” means recursive. So the rm command can remove all the children folders and files of the target folder recursively. “-f” means force. It will ignore non-existent files, and never prompt before removing them. Be careful when you use these two flags together.
The groupdel command is to delete an existing docker user group.
Bonus: Deactivate Network Interface and Ethernet Bridge
If you want to take one step further, you can deactivate the docker0 network interface and delete the docker0 ethernet bridge. Here’s how(Credit: Thanks to anony for mentioning that!😁):
To disable docker0 network interface:
sudo ifconfig docker0 downTo delete the existing docker0 ethernet bridge:
sudo ip link delete docker0The brctl command is deprecated. Updated the above command. Credit to Nicolas Raoul and Søren (Edited on 2024-03-26)
Congratulations! You have just completely removed Docker from your system!
If my note helped, please consider buying me a coffee😁.
Cheers,
Lok
Leave a Reply